Task3G/User Guide/task3G Access
This page was last modified 09:54, 4 March 2008.From Documentation
| Revision as of 05:57, 19 April 2006 Moff (Talk | contribs) (→Capabilities) ← Previous diff |
Current revision Moff (Talk | contribs) (→Roles) |
||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| - | Detailed information on accessing COSMmanager applications can be found in the section COSMmanager Users and Access Controls of the COSMmanager User Guide. The information in this chapter is a summary of the relevant details from that manual. | + | Detailed information on accessing COSmanager applications can be found in the section COSmanager Users and Access Controls of the COSmanager User Guide. The information in this chapter is a summary of the relevant details from that manual. |
| - | To access COSMmanager, a user must first have a UNIX account on the same host as COSMmanager, or on a networked host. To actually run any COSMmanager applications, users must have access rights to the required COSMmanager menus and options. | + | To access COSmanager, a user must first have a UNIX account on the same host as COSmanager, or on a networked host. To actually run any COSmanager applications, users must have access rights to the required COSmanager menus and options. |
| <br> | <br> | ||
| === Roles === | === Roles === | ||
| + | [[Image:Task img 3.jpg|frame|Figure 4 — Capabilities and roles]] | ||
| - | COSMmanager access is controlled by assigning to selected users one or more roles. Roles equate to responsibilities shared by some staff. Each role translates to a set of capabilities that determine users’ access to menus and functions in individual COSMmanager | + | COSmanager access is controlled by assigning to selected users one or more roles. Roles equate to responsibilities shared by some staff. Each role translates to a set of capabilities that determine users’ access to menus and functions in individual COSmanager |
| applications. | applications. | ||
| Line 12: | Line 13: | ||
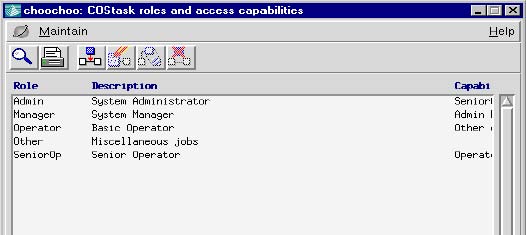
| Task3G is supplied with a set of default roles such as those shown in the diagram below. These roles can be modified to more accurately reflect the needs of an installation. | Task3G is supplied with a set of default roles such as those shown in the diagram below. These roles can be modified to more accurately reflect the needs of an installation. | ||
| - | |||
| - | Figure 4 — Capabilities and roles | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
| + | |||
| === Capabilities === | === Capabilities === | ||
| COSmanager applications such as task3G ‘interpret’ each one of a user’s roles, to determine what capabilities are granted to the user in that application. | COSmanager applications such as task3G ‘interpret’ each one of a user’s roles, to determine what capabilities are granted to the user in that application. | ||
| + | {{note| By convention, role names use initial capitals (“Admin”) and capabilities do not (“submit“).}} | ||
| + | The capabilities associated with roles in task3G can be viewed and modified by users with top-level privileges only. Examples of capabilities used within task3G are shown in the table below and the full set can be viewed under {{cnav|task3G configuration > Tables > Roles}}. | ||
| - | ---- | + | :{| border="0" cellpadding="3" cellspacing="0" |
| - | ;Note: By convention, role names use initial capitals (“Admin”) and capabilities do not (“submit“). | + | ! align="left" width="100" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | Capability |
| - | ---- | + | ! align="left" width="250" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Description |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | The capabilities associated with roles in task3G can be viewed and modified by users with top-level privileges only. Examples of capabilities used within task3G are shown in the table below and the full set can be viewed under task3G configuration > Tables > Roles. | + | |
| - | + | ||
| - | + | ||
| - | {| border="1" cellpadding="8" cellspacing="0" | + | |
| - | !Capability | + | |
| - | !Description | + | |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |clr_status | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | clr_status |
| - | |Ability to manually clear job status | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Ability to manually clear job status |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |control | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | control |
| - | |Control task3G jobs and tasks | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Control task3G jobs and tasks |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |disable | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | disable |
| - | |Ability to disable/enable jobs | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Ability to disable/enable jobs |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |display | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | display |
| - | |Display contents of task3G tables | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Display contents of task3G tables |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |kill | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | kill |
| - | |Ability to cancel and kill jobs and tasks | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Ability to cancel and kill jobs and tasks |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |killall | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | killall |
| - | |Ability to kill any task | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Ability to kill any task |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |maintain | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | maintain |
| - | |Maintain task3G tables | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Maintain task3G tables |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |runall | + | | valign="top" style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;border-right:1px solid grey;" | runall |
| - | |Access to all jobs enabled | + | | style="border-bottom:1px solid grey;" | Access to all jobs enabled |
| |- | |- | ||
| - | |submit | + | | valign="top" style="border-right:1px solid grey;" | submit |
| - | |Ability to submit task3G jobs | + | | Ability to submit task3G jobs |
| |} | |} | ||
| - | |||
| From this example, users without maintain capability should not be able to maintain | From this example, users without maintain capability should not be able to maintain | ||
| Line 69: | Line 62: | ||
| === Steps to Obtaining Access to task3G === | === Steps to Obtaining Access to task3G === | ||
| - | #Add user to COSMmanager as either a user or a group. | + | #Add user to COSmanager as either a user or a group. |
| - | #Assign appropriate COSMmanager roles to the user, creating new role if required. | + | #Assign appropriate COSmanager roles to the user, creating new role if required. |
| - | #Ensure capabilities assigned to role within task3G are adequate by examining the ‘task3G Access Capabilities and Roles’ table under task3G configuration > Tables > Roles. Amend or add roles as required. | + | #Ensure capabilities assigned to role within task3G are adequate by examining the ‘task3G Access Capabilities and Roles’ table under {{cnav|task3G configuration > Tables > Roles}}. Amend or add roles as required. |
Current revision
Detailed information on accessing COSmanager applications can be found in the section COSmanager Users and Access Controls of the COSmanager User Guide. The information in this chapter is a summary of the relevant details from that manual.
To access COSmanager, a user must first have a UNIX account on the same host as COSmanager, or on a networked host. To actually run any COSmanager applications, users must have access rights to the required COSmanager menus and options.
Roles
COSmanager access is controlled by assigning to selected users one or more roles. Roles equate to responsibilities shared by some staff. Each role translates to a set of capabilities that determine users’ access to menus and functions in individual COSmanager applications.
By grouping users with similar access requirements and responsibilities, you can avoid having to allocate capabilities to individual users and security is enhanced by granting access rights according to job function, rather than to transient individuals.
Task3G is supplied with a set of default roles such as those shown in the diagram below. These roles can be modified to more accurately reflect the needs of an installation.
Capabilities
COSmanager applications such as task3G ‘interpret’ each one of a user’s roles, to determine what capabilities are granted to the user in that application.
| Note | |
| By convention, role names use initial capitals (“Admin”) and capabilities do not (“submit“). | |
The capabilities associated with roles in task3G can be viewed and modified by users with top-level privileges only. Examples of capabilities used within task3G are shown in the table below and the full set can be viewed under task3G configuration > Tables > Roles .
Capability Description clr_status Ability to manually clear job status control Control task3G jobs and tasks disable Ability to disable/enable jobs display Display contents of task3G tables kill Ability to cancel and kill jobs and tasks killall Ability to kill any task maintain Maintain task3G tables runall Access to all jobs enabled submit Ability to submit task3G jobs
From this example, users without maintain capability should not be able to maintain any duty or access task3G configuration.
Steps to Obtaining Access to task3G
- Add user to COSmanager as either a user or a group.
- Assign appropriate COSmanager roles to the user, creating new role if required.
- Ensure capabilities assigned to role within task3G are adequate by examining the ‘task3G Access Capabilities and Roles’ table under task3G configuration > Tables > Roles . Amend or add roles as required.