Duty3G/Duty3G 5.1 Release Notes
From Documentation
| Revision as of 11:25, 20 September 2006 Moff (Talk | contribs) (→Upgrading duty3G) ← Previous diff |
Revision as of 12:15, 20 September 2006 Moff (Talk | contribs) (→Upgrading duty3G) Next diff → |
||
| Line 95: | Line 95: | ||
| :This completes the upgrade installation. You must now restart COSmanager for the new version of duty3G to come into affect. | :This completes the upgrade installation. You must now restart COSmanager for the new version of duty3G to come into affect. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | == Technical Notes: Using duty3G V5.1 == | ||
| + | |||
| + | This section contains some technical notes and tips about using duty3G V5.1. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Temporary or trial licensing''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Duty3G may be issued with a temporary license for use in trials or demonstrations. Temporary licenses have an in-built expiry date. You must obtain a permanent license or a new temporary license from your COSMOS distributor to keep using COStask after the expiry date.NoteCOStask won’t install if the license key is due to expire within the next 7 days. In this case you will need to obtain a new license key from your COSMOS distributor. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''COSMOS framework version required for duty3G V5.1''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Duty V5.1 requires COSMOS V4.2.5 or newer. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Some platforms do not support all QUEUE features''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Because duty3G uses the standard AT queues for job submission, any limitations in a platform’s implementation of AT queues may cause corresponding limitations in COStask’s queues. In particular some platforms restrict the number of queues available for use (for example HP/UX and DEC Unix), while some do not allow the specification of the maximum number of concurrent jobs (for example Linux). In most cases these limitations are very minor, and will only affect your site if you want to define new queues. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''The QUEUEDEFS file''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | Most implementations of AT use a file called either /usr/lib/cron/queuedefs or /var/adm/cron/queuedefs. When COStask is installed, all existing entries in the QUEUEDEFS file are made available as COStask queues. Also, an extra AT queue, “t” is added for the main COStask queue. (On DEC Unix queue “f” is used instead, as queues beyond “f” are not permitted). After installation, QUEUEDEFS should NOT be edited directly, rather COStask’s queue maintenance (under COStask Configuration) should be used instead. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Schedules and Schedtime''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | When duty3G V5.1 is installed on a system with a version of COSMOS V3.2.X, some new framework facilities are added to support more generalised scheduling. These include the datelist and schedule tables, which supersede the schedtime table (used in COStask V4.0). When the schedule table is installed, any locally added entries are copied into the schedule table. However, it is important to note that the schedtime and schedule tables are maintained separately, and so changes to one table will not be reflected in the other.If you are running COSMOS V3.2.X, the schedule and datelist tables can only be maintained from the COStask Configuration window.It is possible to update the schedule table with any new entries added to the schedtime table by running the program upg_sched which is installed in the COSMOS Install directory. Note however that this will NOT detect changes to existing entries in schedtime. | ||
| + | |||
| + | <br> | ||
| + | '''Audit Trails and Logfiles''' | ||
| + | |||
| + | When duty3Gis installed, two new audit trails are created: duty_log and duty_compl. By default, these are created in the system spool area (usually /usr/spool or /var/spool).COStask is the primary audit trail, recording many actions that COStask performs:•Job Submission;•Start and end of job and task execution;•Most operator actions (cancel, hold etc.).Tasklog is used to hold all the logfiles created when a job or task executes. Depending on the amount of output produced by your jobs, this directory may become large, so it is important that audit trail cycling be configured correctly for your site to prevent these files from growing unbounded | ||
| <br> | <br> | ||
Revision as of 12:15, 20 September 2006
Contents |
Overview and Features
Duty3G
Duty3G V5.1 encourages sound management practices by making it possible to perform the regular operations workload on UNIX, Linux and Windows servers in a way that is efficient, reliable, verifiable, compliant, and repeatable whilst protecting privileged user access. With duty3G you assign the privilege to the duty, and then assign the duty to the user.
New features in Duty3G V5.1
Key features of the new release are:
Enhanced operations
- Enhanced schedules, for example, a Weekday schedule can now exclude public holidays.
- You can now assign duties to a class/folder, so the duty name no longer needs to be prefixed with a Class or Category. Now it is much easier to locate that ‘XYZ’ duty.
- You can now order duties in the order they should be performed, so the duty name no longer needs to be prefixed with a Sequence number
- You can now force the user to re-authenticate before running certain duties giving added security.
- Duties can now be auto disabled and/or auto re-enabled on given dates. This is useful during system rollouts or migration projects.
- Duties are now run asynchronously, meaning if you have a long running duty it no longer stops you from running another duty.
- As a duty is performed, that duty is now “locked” so no other user can run the same duty with possible undesirable results.
- End user's can set their own start-up view (at-request or outstanding duties) and start-up Class, along with a reminder period before duties become overdue.
- End user’s can now view upcoming scheduled duties for a selected day or date in the future – “What has to be done on Friday?”. This is also useful for Administrators to check that duties have been scheduled correctly, for example, making sure certain duties are not scheduled for Christmas Day.
- You can now filter your view of duties:
- for a selected class
- that run on a selected host
- for a selected users' role
Improved auditing
- Filtering has been added to make viewing the Duty audit trail more meaningful:
- by selected time period
- that have ended in error
- for selected duty
- for selected user
- for selected mode
- Duty audit trail entries are now colour coded to make it easier to spot abnormal entries.
- New duty compliance reports are generated daily and can be viewed at any time. These reports highlight failed, missed and skipped duties – exceptions that affect operations compliance.
Documentation
- An HTML or text document can now be associated with a duty, so end users can see what Policies and Procedures the duty is supporting.
- You can now link directly to online help (user guide), release notes and other documentation, and even report a bug via duty3G
Installation Requirements
Software prerequisites
To install and run Duty3G V5.1 on a host, you must have:
- COSmanager V4.2.5 or later already installed on the host (see the COSmanager User Guide for instructions)
- a duty3G distribution
- a valid license key for this host (see your COSmanager distributor if you don’t have a valid license key)
- sufficient disk space
- COSmanager Manager access, or equivalent
- the ability to open a root shell
Disk space required
| Software | Approximately 1 MB in the duty3G home directory. |
|---|---|
| Temporary Files | While installing duty3G: less than 1 MB, to hold a copy of the software distribution. While duty3G is running: less than 1 MB in /tmp. |
| Audit Trail | For the duty3G audit trail, about 10 - 50 MB in the system spool area. The actual amount will depend on the activity on your system (e.g. how many duties are run), and how often you archive and delete the log files. |
| Compliance Reports | For the duty3G compliance reports, about 5 - 20 MB in the system spool area. |
Running Remote Duties on Windows
The current duty3G release supports running remote duties on Windows hosts which have the EWC (Enterprise Windows Client) V3.1.1 installed. This product may be purchased separately.
Upgrading duty3G
- Download the distribution file to /tmp on the target host.
- From the Configuration menu, select COSmanager configuration > Applications.
- Select Application > Install.
- Press Choose. You will see a list of the applications that can be installed. Choose the entry titled duty3G, and press Accept.
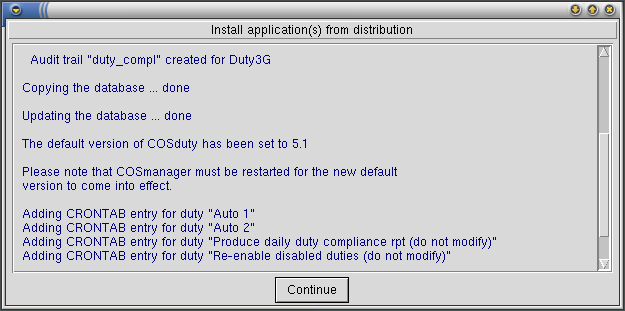
- COSmanager copies the duty3G files from the distribution file to the target directory, updates the duty3G audit trail and creates the duty3g compliance report directory.
- To migrate your existing COSduty 3.0 database to the newly installed version press Copy. Your existing database is copied and updated with new table columns.
- To make the newly install duty3G the default version press Accept, then press Continue.
- Any automatic duties are added or re-added to the cosmos crontab.
- This completes the upgrade installation. You must now restart COSmanager for the new version of duty3G to come into affect.
Technical Notes: Using duty3G V5.1
This section contains some technical notes and tips about using duty3G V5.1.
Temporary or trial licensing
Duty3G may be issued with a temporary license for use in trials or demonstrations. Temporary licenses have an in-built expiry date. You must obtain a permanent license or a new temporary license from your COSMOS distributor to keep using COStask after the expiry date.NoteCOStask won’t install if the license key is due to expire within the next 7 days. In this case you will need to obtain a new license key from your COSMOS distributor.
COSMOS framework version required for duty3G V5.1
Duty V5.1 requires COSMOS V4.2.5 or newer.
Some platforms do not support all QUEUE features
Because duty3G uses the standard AT queues for job submission, any limitations in a platform’s implementation of AT queues may cause corresponding limitations in COStask’s queues. In particular some platforms restrict the number of queues available for use (for example HP/UX and DEC Unix), while some do not allow the specification of the maximum number of concurrent jobs (for example Linux). In most cases these limitations are very minor, and will only affect your site if you want to define new queues.
The QUEUEDEFS file
Most implementations of AT use a file called either /usr/lib/cron/queuedefs or /var/adm/cron/queuedefs. When COStask is installed, all existing entries in the QUEUEDEFS file are made available as COStask queues. Also, an extra AT queue, “t” is added for the main COStask queue. (On DEC Unix queue “f” is used instead, as queues beyond “f” are not permitted). After installation, QUEUEDEFS should NOT be edited directly, rather COStask’s queue maintenance (under COStask Configuration) should be used instead.
Schedules and Schedtime
When duty3G V5.1 is installed on a system with a version of COSMOS V3.2.X, some new framework facilities are added to support more generalised scheduling. These include the datelist and schedule tables, which supersede the schedtime table (used in COStask V4.0). When the schedule table is installed, any locally added entries are copied into the schedule table. However, it is important to note that the schedtime and schedule tables are maintained separately, and so changes to one table will not be reflected in the other.If you are running COSMOS V3.2.X, the schedule and datelist tables can only be maintained from the COStask Configuration window.It is possible to update the schedule table with any new entries added to the schedtime table by running the program upg_sched which is installed in the COSMOS Install directory. Note however that this will NOT detect changes to existing entries in schedtime.
Audit Trails and Logfiles
When duty3Gis installed, two new audit trails are created: duty_log and duty_compl. By default, these are created in the system spool area (usually /usr/spool or /var/spool).COStask is the primary audit trail, recording many actions that COStask performs:•Job Submission;•Start and end of job and task execution;•Most operator actions (cancel, hold etc.).Tasklog is used to hold all the logfiles created when a job or task executes. Depending on the amount of output produced by your jobs, this directory may become large, so it is important that audit trail cycling be configured correctly for your site to prevent these files from growing unbounded